
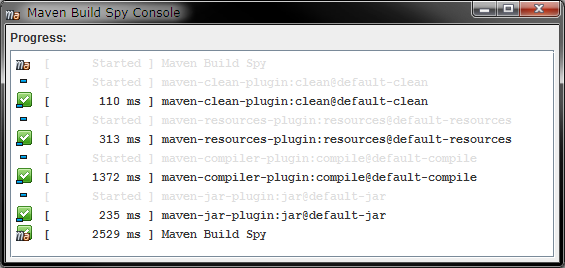
The solution turned out to be related to the wonderful world of Maven classloaders. The problem was that each of the product modules would log that they would be deployed at the end of the build, but after the last module ran its deploy phase, nothing would happen - no uploading of artifacts would be attempted, no warnings or debug messages logged to explain the inaction, and the build would just end with a SUCCESS status. The other modules were also configured to use the deployAtEnd parameter of the parent’s maven-deploy-plugin plugin configuration. What was different about this module versus the others was that it did not use the root POM as a parent (as it was sufficiently different from the other more product-focused modules).
MAVEN INSTALL GOAL CODE
This module’s reposibility was to run some code health checks using Google’s error-prone static analysis tool to catch some programming mistakes that our developers occassionally made that had a negative effect at runtime. What was odd was that no error of any kind was being communicated, even in DEBUG mode.Įxamining the history of the repository, what had changed was the addition of a new module (“slbugs”) to the existing multi-module Maven build. Because, the order of execution is completely dependent on the order of the goals defined.At SnapLogic, we recently noticed that a particular build job that was responsible for deploying build artifacts to a Nexus repository via Maven had suddenly stopped, well, deploying. Only thing that matters is the order of the goals defined for a given project in pom.xml. A goal in maven can be associated to zero or more build phases. Goal in maven is nothing but a particular task which leads to the compiling, building and managing of a project. Click on th link below to download.ĭownload Super POM Xml file Goals in Maven This will come as a default one with the maven installation.Ī typical super pom.xml can be found in the attached file. This super pom.xml is not required to be written by the developers. This super pom.xml basically defines a set of default configurations which is shared and used by all the maven projects. As the maven 2 version was introduced, this was renamed to pom.xml Super POMĪll the maven projects pom.xml files always extends the super pom.xml file. NOTE : Actually pom.xml was earlier used in the name of project.xml in maven 1. This will enable the maven to read all the configurations made, build profiles defined, repositories configured and all other important details and then executes the task accordingly. Whenever it comes for executing a task for a project, maven scans through the entries made in the pom. version - This element is used to derive the version of any project in order to classify the versions as and when the major changes/implementations are carried during the development phase of a project.artifactId - Even though the name says as "id", this is basically defines the name of any project.groupId - as the name itself shows that this is an id which is unique for any project in an organization.Developers should ensure to define the below list of elements which are known as maven co-ordinates before defining a pom.xml file: Dependencies used in the projects (Jar files)Ī typical pom.xml of simple java project will look like as shown in the below figure.Ī pom.xml will always start with the root element called under which all the other required configurations will be made.
In simple, it contains the details of the build life cycle of a project.īelow are some of the configurations that can be handled in the pom.xml file : It contains all the necessary information about the configuration details, dependencies included and plug-ins included in the project. The pom.xml basically contains the information related to the project which is built or to be built in.

This file represents the very basic and fundamental unit in maven. This pom.xml will always be located in the root directory of any maven project. Basically any maven project consists of one configurable file called pom.xml, which stands for the abbreviation Project Object Model. The easiest way to describe a POM in a maven project is, it is nothing but the core element of any maven project.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
